A recent paper published in the well-known journal Nutrients agrees with our conference aims. Discuss the health effects of wine as one of the Mediterranean Diet components. According with Paola Ditano-Vázquez and co-authors low-to-moderate consumption of red wine with meals and virgin olive oil have been reported to prevent cardiometabolic diseases, including CVD, T2DM, MetS and obesity. Current mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of the MedDiet include a reduction in inflammatory and oxidative stress markers, improvements in lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and endothelial function, as well as antiatherosclerotic and antithrombotic properties, mainly attributable to their polyphenols content.

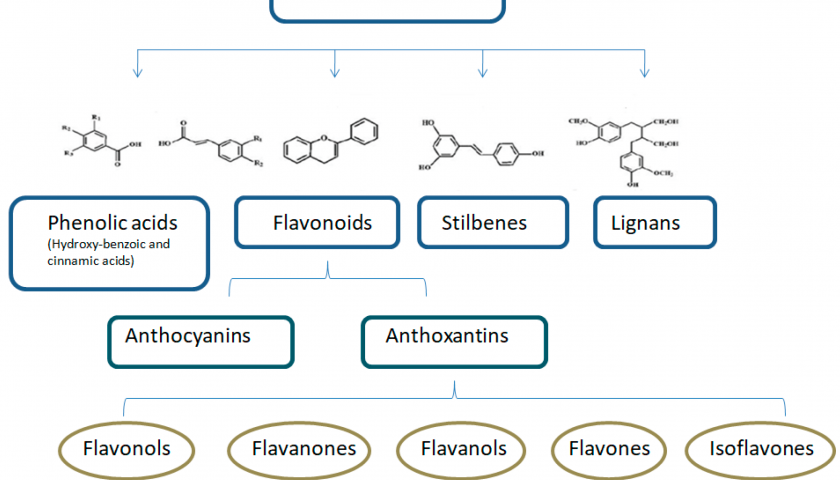
A growing interest has emerged in the beneficial effects of plant-based diets for the prevention of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and obesity. The Mediterranean diet, one of the most widely evaluated dietary patterns in scientific literature, includes in its nutrients two fluid foods: olive oil, as the main source of fats, and a low-to-moderate consumption of wine, mainly red, particularly during meals. Current mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of the Mediterranean diet include a reduction in inflammatory and oxidative stress markers, improvement in lipid profile, insulin sensitivity and endothelial function, as well as antithrombotic properties. Most of these effects are attributable to bioactive ingredients including polyphenols, mono- and poly-unsaturated fatty acids. Polyphenols are a heterogeneous group of phytochemicals containing phenol rings. The principal classes of red wine polyphenols include flavonols (quercetin and myricetin), flavanols (catechin and epicatechin), anthocyanin and stilbenes (resveratrol). Olive oil has at least 30 phenolic compounds. Among them, the main are simple phenols (tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol), secoroids and lignans. The present narrative review focuses on phenols, part of red wine and virgin olive oil, discussing the evidence of their effects on lipids, blood pressure, atheromatous plaque and glucose metabolism. Read this paper.